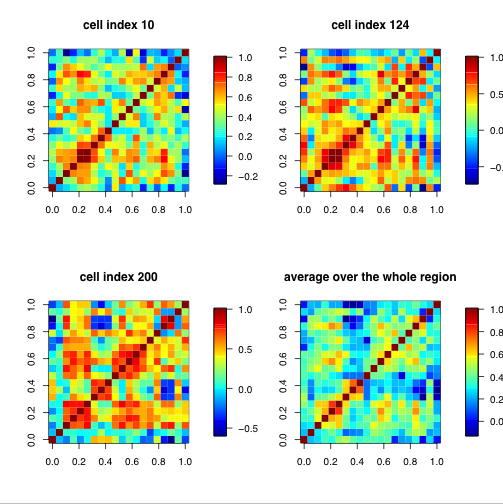
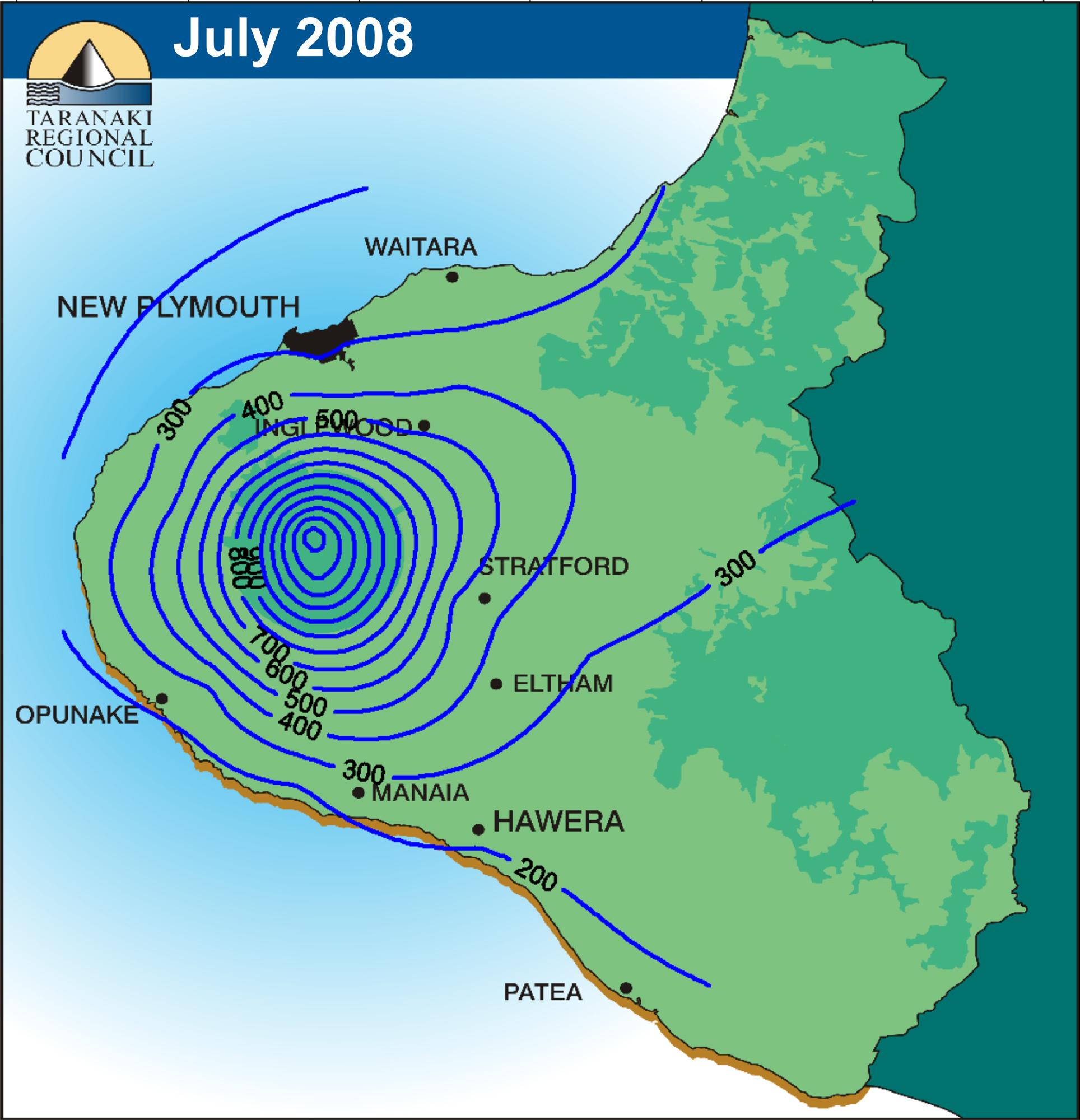
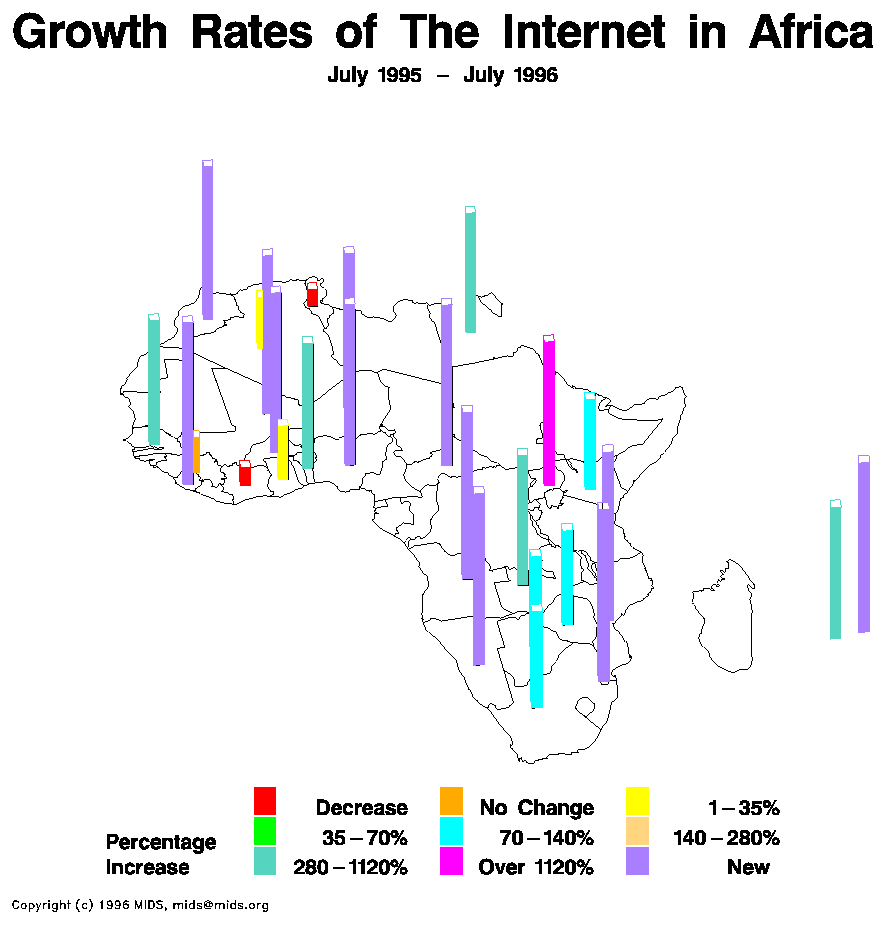
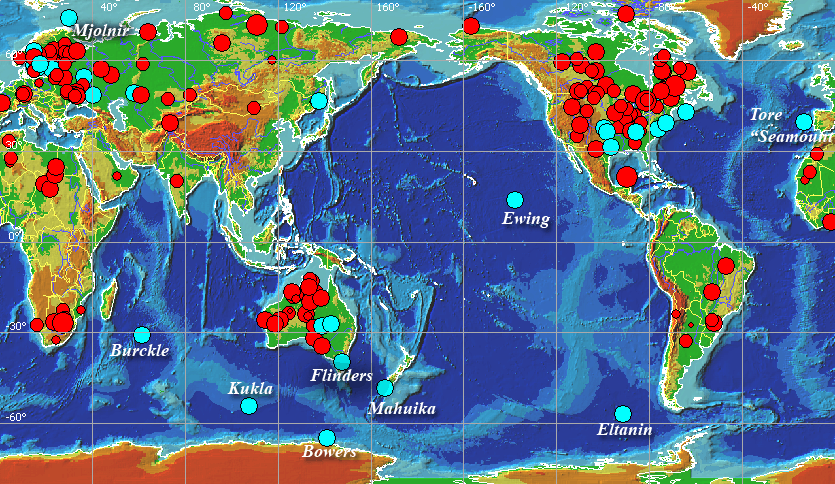
A correlation matrix is a relationship between variables that may be negative, positive, or curved. Correlation is measured and expressed by using numeric scales. It is a that matrix gives the correlations between all pairs of data sets.This example of a correlation matrix is with 20 different climate models at specific geographical locations. Each row and column of the matrix represents one of the 20 models in the study.